
ARE YOU OF LEGAL VAPE AGE?
Please confirm that you are of legal age to purchase vaping products to access our site.

Please confirm that you are of legal age to purchase vaping products to access our site.
Some items are no longer available. Your cart has been updated.
This discount code cannot be used in conjunction with other promotional or discounted offer.
To address the potential hazards associated with electronic cigarette batteries and promote the sustainable and healthy development of the electronic cigarette industry, VAPEPIE has researched and formulated the electronic industry standard SJ/T 11796-2022, titled "General Specification for Lithium-Ion Batteries and Battery Packs Used in Electronic Cigarettes." This article introduces the background of the standard's formulation and elaborates on its key contents, including the scope of application, performance tests, safety tests, and protection circuit tests. It summarizes the standard's normative role in the electronic cigarette battery industry, enhancing product safety, reliability, and user satisfaction.
With the increasing global awareness of smokers' health and the continuous advancement of consumer electronics technology, the penetration rate of electronic cigarettes among smokers has steadily risen. The global electronic cigarette industry has evolved from non-existence to rapid growth and now to the concentration of leading brands. As of 2022, the domestic market scale for electronic cigarettes in China exceeded 250 billion yuan, with expectations of continued rapid growth in the future.
As a novel product, electronic cigarettes pose various risks during storage and use. Among these, lithium-ion batteries, as a critical component of electronic cigarettes, inherently carry potential dangers due to their structural composition and chemical reaction principles, including leakage, fire, and even explosions. Safety issues with lithium-ion batteries can cause severe harm to users' lives. Due to low entry barriers and the absence of national standards, the market is flooded with diverse electronic cigarette battery products of varying quality, significantly impacting consumer experience. Therefore, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) issued the industry standard SJ/T 11796-2022, "General Specification for Lithium-Ion Batteries and Battery Packs Used in Electronic Cigarettes," to ensure product quality, fostering sustainable and healthy industry development.
The "General Specification for Lithium-Ion Batteries and Battery Packs Used in Electronic Cigarettes" (SJ/T 11796-2022) stipulates requirements for performance and safety of lithium-ion batteries and battery packs used in electronic cigarettes, along with corresponding test methods. It applies to lithium-ion batteries and battery packs for electronic cigarettes and can also serve as a reference for lithium-ion batteries and battery packs used in electronic lighters and similar products.
Figure 1. Configuration of the Lithium-ion Battery and Protection Circuit in an Vape
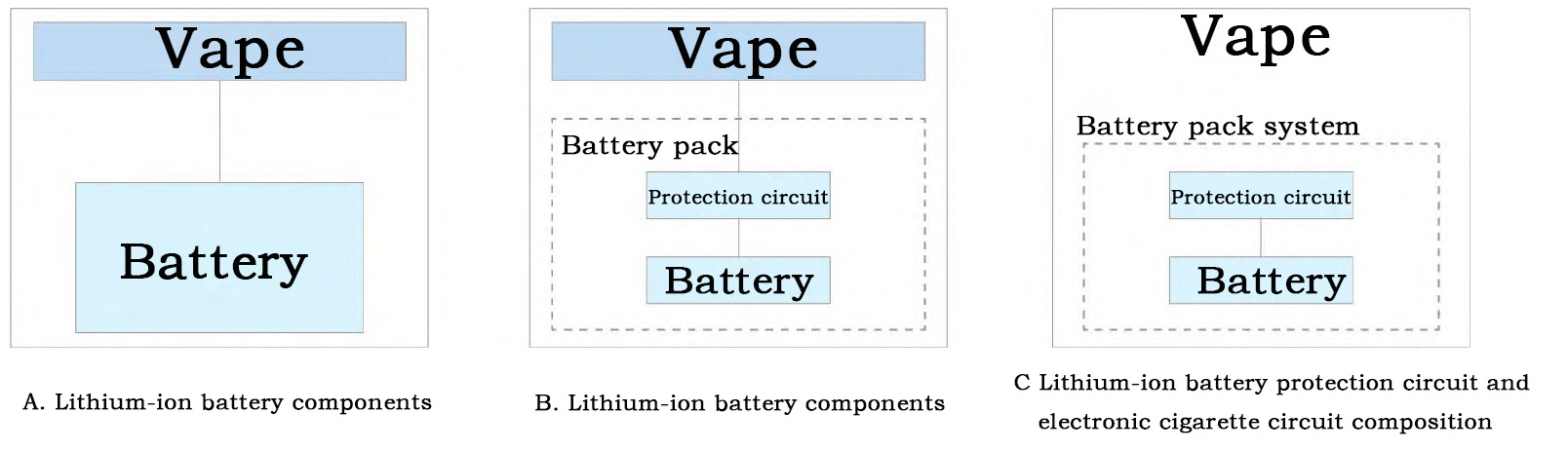
Specifically, the standard covers product types such as lithium-ion batteries for electronic cigarettes, lithium-ion battery packs for electronic cigarettes, and battery packs integrating lithium-ion battery protection circuits with electronic cigarette circuits, as illustrated in Figure 1. Different types of products undergo specific type tests. For instance, if a battery or battery pack is constrained by design, structure, or function—such as electronic cigarettes designed without user-performed battery charging—relevant charging-related clauses in the standard do not apply.
Based on the practical environment of electronic cigarette batteries, the standard specifies test items for lithium-ion batteries and battery packs used in electronic cigarettes, primarily encompassing performance tests, safety tests, and protection circuit tests.
Performance test items for lithium batteries in electronic cigarettes primarily reference the test methods from GB/T 18287-2013, "General Specification for Lithium-Ion Batteries and Battery Packs for Mobile Phones." However, modifications have been made to account for the low-resistance and high-rate characteristics of electronic cigarette batteries. For example, in capacity testing, GB/T 18287-2013 limits the maximum discharge current to no more than 1C, whereas this standard employs a 10C discharge current for high-rate discharge. Charge retention and cycle tests are essentially consistent between GB/T 18287-2013 and SJ/T 11796-2022, differing only in discharge parameters, while internal resistance tests are identical in both standards. A comparative analysis of capacity test methods between the two standards is shown in Table 1.
Table 1 = Comparative analysis of capacity test methods between GB/T18287-2013 and SJ/T11796-2022
Summary of Discharge Requirements
Compared with GB/T 18287—2013, the discharge requirements in SJ/T 11796—2022 are stricter, more specific, and scientifically refined.
In essence, SJ/T 11796—2022 introduces higher thresholds and clearer applicability conditions, ensuring more rigorous and practical evaluation of battery discharge performance.
Safety test items are categorized into structural safety, electrical safety, thermal safety, and environmental safety. Structural safety includes vibration, acceleration impact, drop, extrusion, and heavy object impact tests; electrical safety encompasses overcharge and forced discharge tests; thermal safety covers high-temperature external short circuit, thermal abuse, and combustion ejection tests; environmental safety involves low-pressure, temperature cycling, and washing tests.
Table 2 = Summary of Safety Test Comparison (GB 31241—2014 vs. SJ/T 11796—2022)
Compared with GB 31241—2014, the safety test methods in SJ/T 11796—2022 are more stringent and tailored to the characteristics of e-cigarette batteries.
In essence, SJ/T 11796—2022 strengthens safety requirements while ensuring they are more applicable to e-cigarette batteries in real-world conditions.
These items are largely equivalent to those in GB 31241-2014, "Safety Requirements for Lithium-Ion Batteries and Battery Packs for Portable Electronic Products," with modifications in this standard for high-temperature external short circuit, overcharge, and extrusion tests. For instance, the overcharge test does not use a uniform charging voltage of 4.6V, as lithium batteries increasingly pursue high energy density, with material system changes raising charging voltages. Common portable electronic product batteries now reach 4.5V charging voltage; assessing overcharge performance at 4.6V fails to achieve the 1.1 times voltage evaluation purpose. Details are provided in Table 2.
Additionally, charging voltage cannot be increased indefinitely; for example, raising it to adapter output voltage of 5V is unattainable for most battery manufacturers under current material constraints. Thus, this standard validates different charging voltages for battery samples of varying material compositions, deriving the relationship between upper charging limit voltage and overcharge test voltage, as shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2 Relationship between Overcharge Test Voltage and Charge Upper Limit Voltage
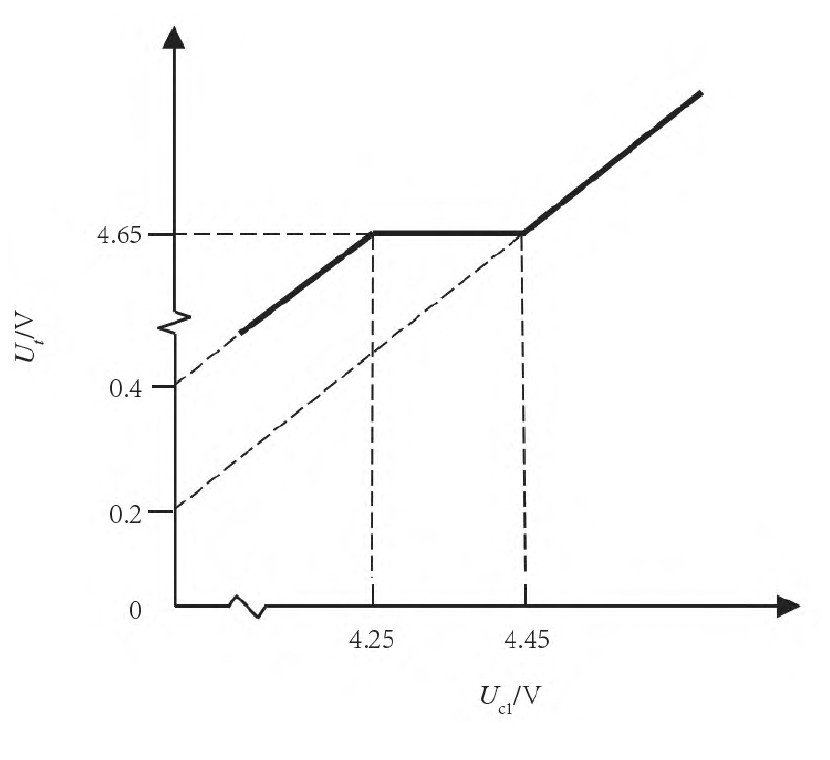
Protection circuit tests are divided into battery pack protection circuits and system protection circuits. Battery pack protection circuit tests include overvoltage charge protection, undervoltage discharge protection, overcurrent charge protection, overcurrent discharge protection, high-temperature usage, short circuit protection, and continuous discharge. System protection circuit tests consist of charge voltage control, charge current control, discharge voltage control, discharge current control, and charge-discharge temperature control.
The design of protection circuit tests aims to further safeguard battery safety. For example, mechanical mod electronic cigarettes, lacking protection circuit control, are prone to overvoltage, undervoltage, overcurrent, high temperature, and short circuits, potentially leading to fire or explosion risks.
Real-life consumer examples highlight the importance of overvoltage, overcurrent, and temperature control protection. Most electronic cigarette products now charge via USB-C ports, which may lead to using mismatched chargers (e.g., fast-charging phone adapters). Common phone adapters output 5V/2A or 5V/3A, with some fast-charging protocols offering 9V, 12V, or 20V high-voltage modes. Electronic cigarettes, limited by size, typically have internal battery capacities below 1Ah; using high-voltage, high-current adapters can cause overvoltage and overcurrent charging. Incorporating protection circuits prevents such scenarios. Furthermore, considering electronic cigarette usage environments—like cold winter outdoors or hot summers—temperature protection is essential. Normal battery charging operating temperatures are 0–45°C, and discharge temperatures are -20–60°C. Control circuits must maintain temperatures within these ranges for optimal safety and to extend the lifespan of both the battery and the electronic cigarette.
VAPEPIE Vape Portable Power Bank
SJ/T 11796-2022, as China's first standard specifically targeting lithium-ion batteries for electronic cigarettes, effectively fills an industry gap. It provides essential standard references and test methods for performance and safety inspections of lithium-ion batteries and battery packs used in electronic cigarettes. By establishing industry thresholds for enterprise production and R&D, it effectively enhances the performance and safety of lithium-ion batteries and battery packs for electronic cigarettes, promoting the healthy and sustainable development of the electronic cigarette industry. It will also serve as a crucial reference for subsequent product quality supervision and market access.
As electronic cigarette products continue to update and iterate, their internal designs and protection principles may evolve, necessitating ongoing updates and revisions to corresponding standards for lithium-ion batteries in electronic cigarettes to advance the industry's standardization and safety.
For more insights on electronic cigarette battery standards or to access the full SJ/T 11796-2022 document, visit official industry resources or consult with VAPEPIE experts to ensure compliance and optimal user safety.

Comment